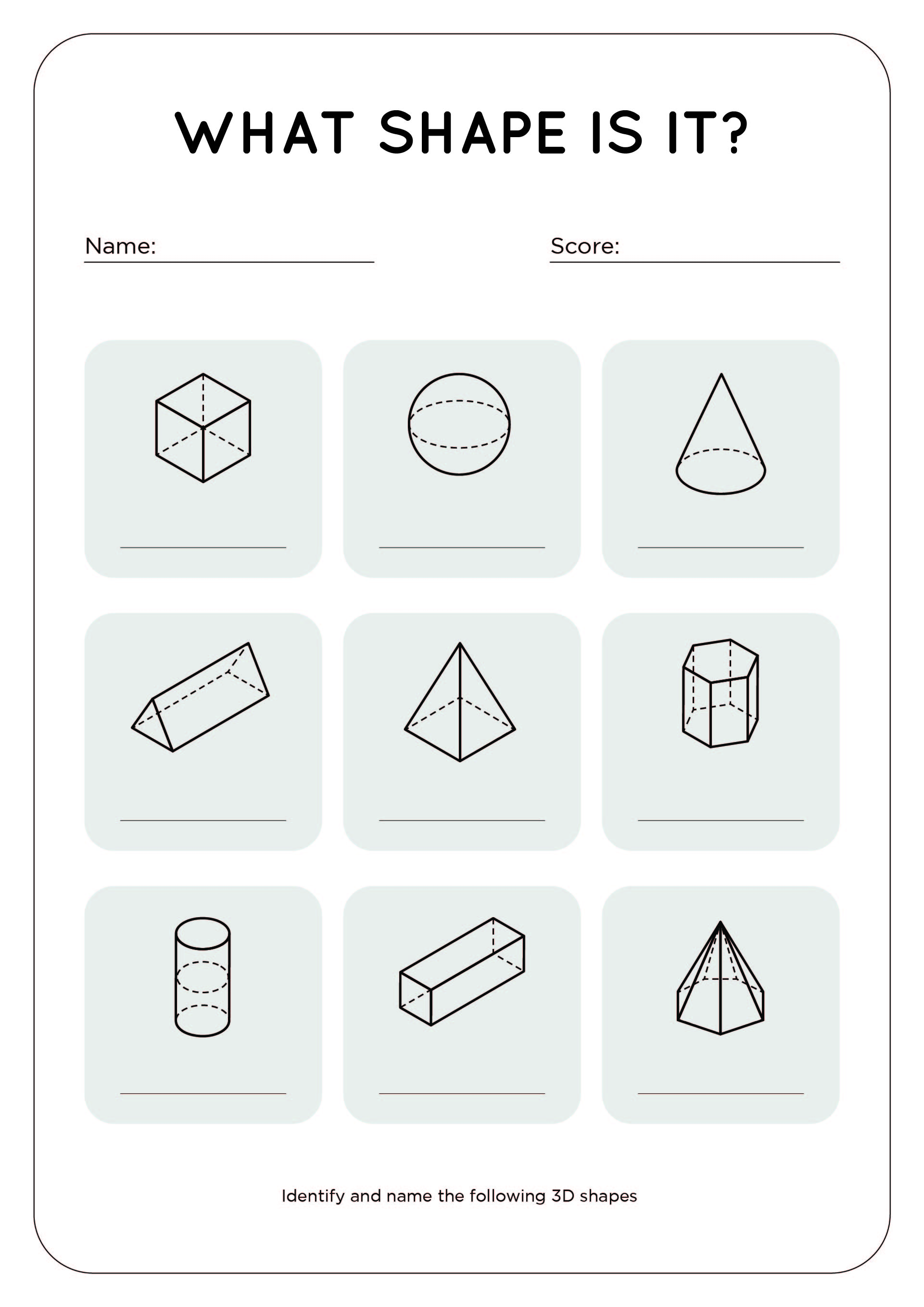
Solids have faces, edges and vertices. The faces are the flat surfaces of solids. The edges are the places where two faces meet. The vertices are the corners. Singular vertex, plural vertices.
Solids are three-dimensional shapes. A prism is a solid, with two parallel faces called bases. The other faces are always parallelograms. The prism is named by the shape of its base. A solid is a pyramid if it has 3 or more triangular faces sharing a common vertex. The base of a pyramid may be any polygon. An edge is formed where two faces meet. A vertex is the point where three or more faces meet.
|
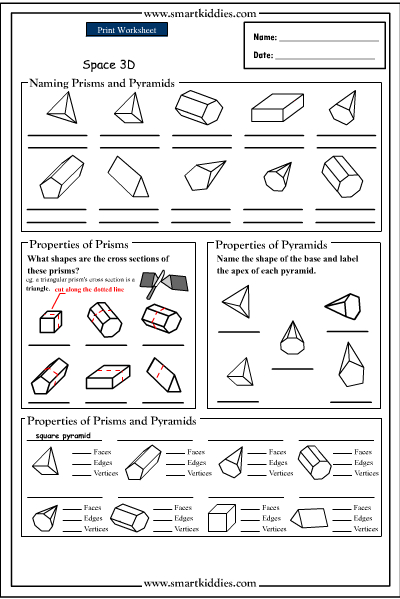
SOLIDS |
SHAPE OF FACES |
|
Square-based pyramid |
1 square at base, 4 triangular faces |
|
Cube |
6 square faces |
|
Cylinder |
|
|
Cone |
|
|
sphere |
|
|
Triangular pyramid/tetrahedron |
|
|
cuboid |
|
|
Triangular based prism |
|
Grade Level: 6
Subject: Mathematics
Topic: Solids (3D Figures)
Duration: 1 Hour
Focus Question: What are the properties of solid figures?
STEM Integration: Engineering (3D modeling), Technology (online geometry tool), Math (geometry), and Science (structures & materials).
Objectives:
By the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
-
Recognize faces, edges, and vertices of solid figures and classify solids according to the number and shape of their faces.
-
Classify solids as prisms and pyramids.
-
Represent and solve problems using geometric models.
Materials/Resources Needed:
3D models or real-life 3D objects
Shape investigation worksheet/chart
Toothpicks and clay/blu tack
Printed shape nets (optional)
Computer/projector for video and digital model
Anchor chart/poster of solid properties
3D models or real-life 3D objects
Shape investigation worksheet/chart
Toothpicks and clay/blu tack
Printed shape nets (optional)
Computer/projector for video and digital model
Anchor chart/poster of solid properties
5E Lesson Plan
1. Engage (10 minutes)
Activity:
-
Show students a short video clip or real-life 3D objects (e.g., cube-shaped box, soccer ball, can, pyramid souvenir).
-
Ask guiding questions:
-
What do you notice about these objects?
-
How are they different from flat shapes?
-
What are some things these objects have in common?
-
STEM Link: Briefly discuss where these shapes appear in real-world engineering designs (buildings, bridges, packaging).
Purpose: To activate prior knowledge and spark curiosity.
2. Explore (15 minutes)
Activity: "Shape Investigation Station"
-
Provide students with physical 3D models (cube, rectangular prism, cylinder, cone, sphere, triangular prism, square pyramid).
-
In pairs, students examine and record:
-
Number of faces, edges, and vertices
-
Type of base
-
Whether it's a prism or pyramid
-
Materials: Solid figures, graphic organizer chart (Face-Edge-Vertex table), Venn diagram template.
Differentiation:
-
Tier 1: Students use labeled models and guided worksheet.
-
Tier 2: Students fill in graphic organizers independently.
-
Tier 3: Students create their own classification chart.
3. Explain (10 minutes)
Discussion and Mini-Lesson:
-
Define key terms: face, edge, vertex, prism, pyramid.
-
Use anchor chart or PowerPoint to reinforce characteristics.
-
Use models to show that prisms have two parallel bases and pyramids have one base with triangular faces.
STEM Link: Use a simple CAD tool (e.g., Tinkercad or GeoGebra) to rotate and label a 3D model virtually.
4. Elaborate (15 minutes)
STEM Application: "Mini 3D Builders"
-
Challenge: In pairs, build their own geometric models using toothpicks and clay/blu tack or 3D shape nets.
-
Students label the faces, edges, and vertices.
-
Extension (Advanced): Describe what would happen if you removed a vertex or added a new edge.
Real-world connection: How are geometric solids used in architecture or packaging design?
Differentiation:
-
Visual aids and scaffolding for students needing support.
-
Enrichment challenge for advanced learners: Create and name an irregular solid.
5. Evaluate (10 minutes)
Three-Tier Evaluation Activity:
| Tier | Task | Objective(s) Assessed |
|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 (Basic) | Identify and label the number of faces, edges, and vertices on a cube and pyramid using a diagram. | Obj. 1 |
| Tier 2 (Proficient) | Classify given shapes as prisms or pyramids and justify your reasoning. | Obj. 1 & 2 |
| Tier 3 (Advanced) | Solve a problem: “A prism has 6 faces and 8 vertices. Draw and name it. Explain how you know.” | Obj. 1, 2 & 3 |
Exit Ticket:
Each student completes a one-question quiz:
-
"What is the difference between a prism and a pyramid?"
Assessment & Differentiation Summary:
-
Use graphic organizers for concrete learners.
-
Pair/group stronger students with those needing support.
-
Include verbal explanation, hands-on modeling, and written work for multiple learning styles.
-
Use tiered tasks to ensure all students can access learning at their level.




No comments:
Post a Comment