Saturday, August 29, 2020
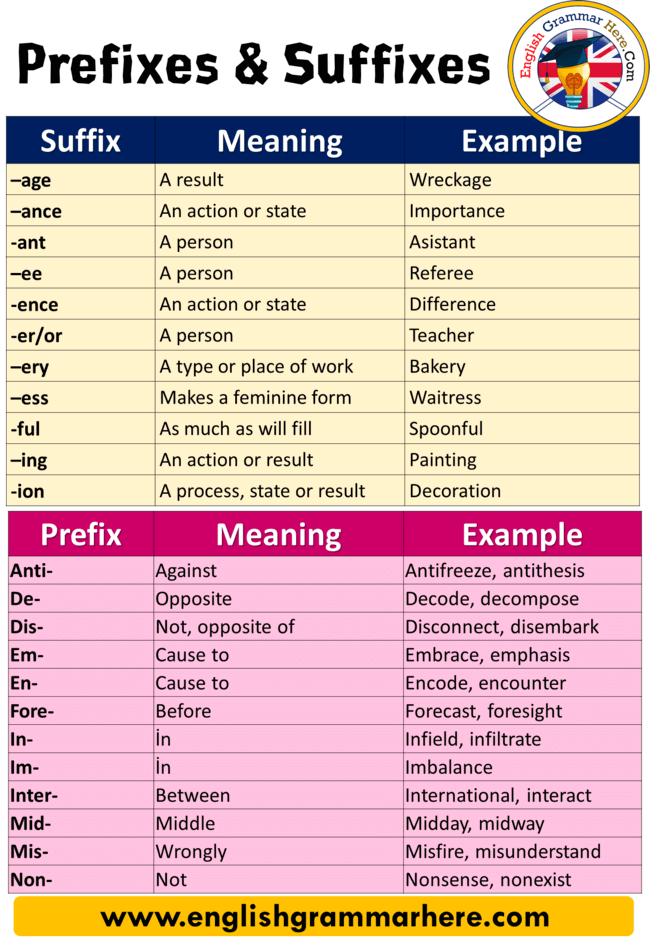
PREFIXES & SUFFIXES
Friday, August 28, 2020
NUMBERS/EXPANDED FORM
How do I write numbers in the different number system?
Read, write and use numbers, using the principle of place value, in the Hindu-Arabic system of numeration.
CONTENT SUMMARY:
We can also write decimals using standard notation.
For example, if our number were 236.82, expanded form and notation would look like this:
200 + 30 + 6 + 0.8 + 0.02 = 236.82
(2 x 100) + (3 x 10) + (6 x 1) + (8 x 1/10) + (2 x 1/100) = 236.82
ENGAGE
1. 1. Write standard numerals for the following:
(a) 40,000 + 9000 + 200 + 60 + 7 = (b) 1,000,000 + 600 + 40 + 2 =
2. 2. Write the following whole numbers in expanded form:
(a) 5,768,965 (b) 786, 944 (c) 32,564, 345
3. 3. Write the highest and smallest number from the following: [78946]
4. 4. What is the highest number that can be formed from 81942, using 9 in the tens place and 4 in the thousands place?
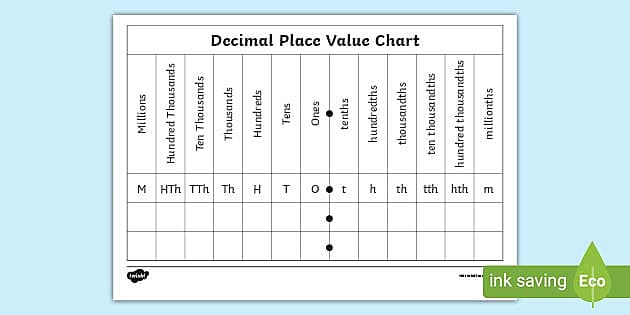
5. What number is represented on the chart below?
(A) 2815.17 (B) 2725.17 (C) 2626.17 (D) 2617.17

Lesson Plan Overview
-
Grade: 6
-
Duration: 1 hour
-
Theme: Numbers – Expanded and Standard Form
-
Focus Question: How do I write numbers in the different number system?
-
Subtopic: Writing numbers in expanded and standard form
-
Numeration System: Hindu-Arabic
-
Objective:
Students will: -
Read, write, and use numbers, using the principle of place value in the Hindu-Arabic system of numeration.
-
Convert between expanded form and standard form.
-
Explain how place value determines the value of each digit.
Materials Needed:
Digit cards (0–9)
Place value charts/ mats
Base ten blocks (real or virtual)
Whiteboards/markers
Printable worksheets, teachers' blogsite
Devices (optional – for STEM tools)
- Projector, chromebooks
🧠 Engage (5–7 minutes)
Activity: "Digit Drama!"
-
Write the number 70,408 on the board.
-
Ask:
-
"Can you tell me the value of each digit?"
-
"What does the 7 represent in this number?"
-
-
Use questioning to spark curiosity:
-
"What happens when I move the 7 from the ten-thousands place to the hundreds place?" (Write: 400,708 vs. 708)
-
Purpose:
To activate prior knowledge on place value and set the stage for expanded/standard form conversion.
🔍 Explore (10–12 minutes)
Activity: "Build a Number – Place Value Flip Cards"
-
Provide students with digit cards (0–9) and place value headings: Millions, Hundred Thousands, Ten Thousands, Thousands, Hundreds, Tens, Ones.
-
In pairs or small groups, have students:
-
Randomly select digits and build a 6-digit number.
-
Write the expanded form on mini whiteboards or chart paper.
-
Share with the class: e.g., 543,210 → 500,000 + 40,000 + 3,000 + 200 + 10
-
STEM Integration:
-
Technology Option: Use an online place value interactive tool (if available) like Didax Virtual Place Value Disks for digital modeling.
-
Engineering Connection: Ask: “How do engineers use numbers in different forms—for measuring, costing, or scaling?”
📘 Explain (10–12 minutes)
Teacher Input:
-
Define standard form and expanded form using anchor charts:
-
Standard Form: The usual way of writing numbers (e.g., 76,032)
-
Expanded Form: Breaking down the value of each digit based on place value (e.g., 70,000 + 6,000 + 0 + 30 + 2)
-
Guided Practice:
-
Model converting:
-
From standard to expanded: 609,004 → 600,000 + 0 + 9,000 + 0 + 0 + 4
-
From expanded to standard: 400,000 + 30,000 + 700 + 2 → 430,702
-
🧠 Elaborate (15 minutes)
Differentiated Activity: "Number Transformation Stations"
Split students into three ability-based groups (can rotate if time allows):
| Tier | Group Name | Task |
|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 (Support) | Place Value Pals | Use base ten blocks/diagrams and teacher support to convert 3-digit and 4-digit numbers between expanded and standard form. |
| Tier 2 (On-level) | Number Ninjas | Convert between 5–6 digit numbers in both directions. Use place value charts. |
| Tier 3 (Extension) | Number Architects | Solve real-life word problems involving population, distance, or cost with large numbers. Convert between expanded and standard forms as part of the explanation. |
Real-World/ STEM Twist:
-
Students use a mock engineering budget:
E.g., “You are building a bridge. Your material costs $245,300. Break it into expanded form to explain how much you’re spending per material type.”
✅ Evaluate (10 minutes)
Three-Tier Evaluation Activity:
| Level | Activity | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 (Basic) | Students convert 3 given numbers between standard and expanded form (up to 4 digits). | At least 2 out of 3 correct conversions. |
| Tier 2 (Proficient) | Students complete a short worksheet with 6 conversions (4-digit and 5-digit numbers) in both directions. | 5 or more correct. |
| Tier 3 (Advanced) | Students are given a word problem: “You’re managing a budget of 1,206,850. Break it down in expanded form and justify your breakdown.” | Logical explanation and accurate expanded form. |
🏁 Extend (Homework/Enrichment)
-
Students research how different number systems (e.g., Roman Numerals or Binary Code) represent the number 365.
-
Optional: Create a poster comparing expanded form vs. Roman numerals.
📌
Thursday, August 27, 2020
NUMBERS / PLACE, FACE, TRUE VALUE
How do I write numbers in the different number system?
Read, write and use numbers, using the principle of place value, in the Hindu-Arabic system of numeration.
Each place on the place value chart represents a power of ten. As we move left of the decimal place, the numbers increase in value. The opposite happens when we move right of the decimal point. All digit to the left of the decimal point are whole numbers. Digits to the right of the decimal point are fractional numbers. Every digit has three values: the place, the face and the actual or true value. The place times the place gives the actual value.
1. (1) Find the difference between the values of the digits underlined.
(a) 567964 (b) 127819
2. (2) Write the following numbers in worded form using place value chart as a guide.
(a) 600606 (a)7487356
3. (3) Robert and Shawn were asked to write the value of each 6 in the number 6666 below. They gave their answers as follow.
|
6 6 6 6 ⇩ ⇩ ⇩ ⇩ 6000 600 60 6
ROBERT |
6 6 6 6 ⇩ ⇩ ⇩ ⇩ 600 60 6 1
SHAWN |
(a) Which of the boys’ response is correct?
(b) Justify your answer.___________________________________________________________
4. (4) Consider the number 1593. Which digit has the greatest value? Give reason for your answer.
5. (5) Place the numbers in the table below in ascending order
|
25496 |
7654 |
1987526 |
340724 |
90063 |
1. 6. Tick true or false for the statements below.
|
STATEMENTS |
TRUE |
FALSE |
|
Each place on the place value chart is 10 times larger than the other. |
|
|
|
The value of each digit in a number depends on its position in the number. |
|
|
|
The value of numbers decrease as we move to the left of the place value chart. |
|
|
|
To get the value of a digit in a number, we multiply the digit by the place it holds on the place value chart. |
|
|
Read given scenario from the chalkboard which will lead to discussion.
|
Paula was asked to find the sum of 4675 and 291. She set out the problem as follows: 4 6 7 5 + 2 9 1 _________ Do you believe Paula will arrive at the correct answer? Yes/No Give reason/s to justify your answer.
|
Lesson Plan: 5E Model (Grade 6)
Theme: Numbers – Place Value, Face Value, True Value
Focus Question: How do I write numbers in the different number system?
Strand: Number
Topic: Place Value, Face Value, True Value
Time: 1 hour
Objectives:
Students will be able to:
-
Read, write, and use numbers using the principle of place value in the Hindu-Arabic system of numeration.
-
Differentiate between face value, place value, and true value of digits in a number.
-
Represent and explain the value of each digit in a given number.
Materials:
-
Place value chart/mats (print/digital)
-
Base-10 blocks or place value disks
-
Whiteboards and markers
-
STEM handout with real-life math data (e.g., population figures, distances in space)
-
Laptops, chromebooks, projector
-
Worksheets for tiered evaluation
Teachers blogsite
STEM Integration:
Math & Technology: Students analyze real-world data such as distances between planets (using large numbers) or country populations and identify place/face/true value of digits using digital place value charts.
The 5E Model
1. Engage (10 mins)
-
Activity: Display the number
7,503,218. Ask:"What do you think each digit means in this number?"
"What happens if we change the position of a digit?" -
Let students use place value flip charts or base-10 blocks to build the number.
-
Discuss face value vs place value briefly using a simple number (e.g.,
408).
2. Explore (15 mins)
-
Students work in pairs to complete a place value scavenger hunt:
-
They are given 3 large numbers (e.g., 5,762,109) and asked to:
-
Identify the face value of specific digits
-
Determine the place value of the same digits
-
Calculate the true value (face value × place value)
-
-
-
Tools: Place value chart, base-10 blocks or an online interactive chart
-
Teacher circulates, prompting with questions:
"What is the digit in the hundred-thousands place?"
"If that digit moved to the tens place, what changes?"
3. Explain (10 mins)
-
Discuss findings from the scavenger hunt.
-
Teacher explicitly teaches:
-
Face value: The digit itself
-
Place value: The position a digit occupies
-
True value: Face value × place value
-
-
Use the number
8,432,105to demonstrate each term with each digit.
4. Elaborate (15 mins)
-
STEM Connection Task:
Provide real-world large numbers (population of Jamaica: ~2,828,000, Earth's distance from Sun: ~149,600,000 km). -
Students:
-
Write numbers in words and figures
-
Identify specific digit values (face/place/true)
-
Discuss why understanding large numbers matters in science/engineering
-
-
Differentiated Task Tiers:
-
Tier 1 (Basic): Identify face, place, and true values of digits in 3-digit and 4-digit numbers
-
Tier 2 (Intermediate): Work with 6- to 7-digit numbers in real-world contexts
-
Tier 3 (Advanced): Given a scenario (e.g., building materials needed for a skyscraper using data with large numbers), analyze and interpret number values in context
-
5. Evaluate (10 mins)
Three-Tier Evaluation Task (choose based on ability group):
| Tier | Task Description |
|---|---|
| Tier 1: Emerging | Identify the face, place, and true value of digits in 3 given numbers (up to 4 digits). |
| Tier 2: Developing | Given a 6-digit number in a real-world context, answer questions such as: “What is the value of the 3 in this number?” |
| Tier 3: Proficient | Given a problem: “The number 4 appears twice in the number 4,840,349. Which one has a greater true value and why?” Students must explain their reasoning. |
Exit Ticket Prompt:
“What is one thing you learned about the Hindu-Arabic number system today?”
“Why is place value important when reading numbers?”
Accommodations for Differentiated Learning:
-
Visual learners: Use base-10 blocks, charts
-
Kinesthetic learners: Build numbers with digit cards
-
Auditory learners: Group discussions and oral explanations
-
Advanced learners: Work with 9-digit numbers and explore exponential notation briefly
Extension/Homework:
-
Students find 3 large numbers from newspapers or online (sports scores, populations, or financial figures) and identify face, place, and true values of any three digits.














![What is Place Value? - [Definition, Facts & Example]](https://cdn-skill.splashmath.com/panel-uploads/GlossaryTerm/752b518abc8344cca04f188f08877a0a/1547028704_Place-Value-Chart-of-Decimal-Numbers-Decrease-left-to-right.png)

